Recently, IAMP, the Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics of Beijing and Sun Yat-sen University have made important progress in the research direction of molecular high-order harmonic generation through close theoretical and experimental cooperation. The research results are entitled "Channel Coupling Dynamics of Deep-Lying Orbitalsin Molecular High-Harmonic Generation", and are published in the journal Physical Review Letters (PHYSICAL REVIEW LETTERS 128, 183202 (2022)) May 6, 2022.
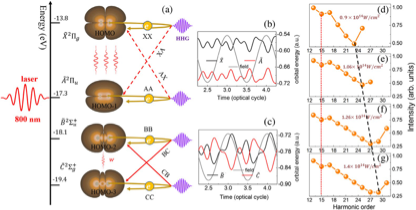
High order harmonic generation (HHG) in high intensity laser field is the basis for obtaining new extreme ultraviolet radiation and attosecond pulse light source, which plays an important role in ultra-fast dynamic detection of quantum system.Understanding the complex multi-electron effects involved in molecular HHG is extremely challenging, and is essential for the development of new technologies such as molecular orbital imaging.In a perfect combination of experimental observations and theoretical simulations, this study reveals a new multi-electron effect that the coupling and interference between different inner orbitals of the CO2molecule leads to a new minimum structure in the low energy region of the harmonic spectrum.This finding suggests that the coupling of inner electron orbitals can be encoded in molecular HHG spectra and generate new characteristic structures. This study will help to achieve accurate regulation of the inner electron and hole dynamics on sub-femtosecond and attosecond time scales.
Dr. Zheng Shu, Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Beijing, and Dr. Hong-Jing Liang, IAMP, are co-first authors of the paper.The corresponding authors are Prof. Ri Ma, IAMP. Associate Professor is Shi-Lin Hu, Sun Yat-sen University, and Prof. Jing Chen, Institute of Applied Physics and Computational Mathematics, Beijing.The research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
(Full text link:https://journals.aps.org/prl/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevLett.128.183202)